Securing your property effectively starts with strategic camera placement. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of key factors to consider when positioning outdoor security cameras for optimal coverage. From understanding field of view and lighting conditions to maximizing signal strength and safety precautions, we’ll explore the essential elements for a robust and reliable security system.
This in-depth guide will walk you through various strategies for positioning outdoor security cameras, taking into account different property types, lighting scenarios, and network considerations. We will delve into the specifics of camera placement, ensuring maximum visibility and minimizing blind spots. The information presented here will assist you in making informed decisions and ultimately maximizing the effectiveness of your outdoor security system.
Camera Placement Strategies

Strategic camera placement is crucial for maximizing the effectiveness of outdoor security systems. Proper positioning ensures comprehensive coverage, allowing for clear identification of individuals and activities within monitored areas. By considering various factors like property size, architectural features, and potential blind spots, homeowners and business owners can create a robust security system.Optimal camera placement significantly enhances the ability to deter criminal activity and provide clear evidence in the event of a security breach.
This meticulous approach translates to a more secure environment and peace of mind for residents and business owners.
Camera Placement Strategies for Different Property Types
Various strategies are employed to optimize camera coverage for different property types. Understanding the specific needs of each property is key to selecting the most effective placement. Consider the unique characteristics of the property when designing the security camera system.
- Large Homes: A comprehensive strategy for large homes involves strategically positioning cameras at entry points, such as garages, front doors, and backyards. Additional cameras can monitor high-traffic areas, such as driveways and pathways, ensuring visibility of all potential access points. Consider mounting cameras on poles or walls for maximum coverage and adaptability to changing conditions. Clear visibility of the property perimeter is vital.
- Small Apartments: In smaller apartment complexes or residences, cameras can be strategically placed to cover entryways, hallways, and common areas. The use of strategically positioned cameras at entrances and exits will provide a clear overview of potential security threats. Consider employing multi-directional cameras to maximize the coverage area with a single camera.
- Businesses: Business security camera systems need to cover entrances, exits, parking lots, and high-traffic areas within the building. Cameras can be mounted on walls, poles, or ceilings, depending on the layout and specific needs of the business. For instance, retail stores may require cameras positioned to monitor cash registers and high-value inventory areas. Consider using wide-angle lenses to ensure comprehensive coverage.
Mounting Options Comparison
Choosing the appropriate mounting option is essential for long-term effectiveness and aesthetics. Various mounting methods offer different advantages and disadvantages.
- Wall-mounted: Wall-mounted cameras are a common and versatile option, suitable for various properties. They are relatively inexpensive and easy to install. However, they might obstruct the view if not positioned correctly. For instance, wall-mounted cameras positioned near windows might not provide optimal visibility if the camera is too close to the window frame. Aesthetics should be considered, especially in residential settings.
- Pole-mounted: Pole-mounted cameras offer greater flexibility and often provide a wider field of view. They are particularly useful for large properties with expansive areas, or for installations where wall-mounted options are not feasible. The poles can be adjusted for optimal viewing angles, but the installation process may be more complex. Maintenance can also be a factor due to the elevated location.
- Ground-mounted: Ground-mounted cameras are ideal for covering ground-level areas, such as parking lots or open spaces. They are effective for detecting activity at the property’s perimeter. However, they may require more significant installation effort and could be vulnerable to vandalism if not properly secured.
Visibility and Blind Spot Management
Addressing blind spots is critical to maximizing security camera coverage. Blind spots can be exploited by individuals looking to avoid detection or commit crimes.
- Entry Points: Cameras should be positioned to provide clear visibility of all entry points, including doors, windows, and gates. Ensure that the cameras have a wide enough field of view to capture the entire entryway and surrounding areas.
- High-Traffic Areas: Cameras should monitor high-traffic areas to deter suspicious activity and record potential incidents. This includes areas such as parking lots, walkways, and entrances.
- Blind Spots: Regularly assess the property to identify potential blind spots. Employ additional cameras or reposition existing ones to ensure comprehensive coverage. Employing motion detectors can help compensate for some blind spots by alerting security personnel to potential threats.
Recommended Camera Placement Strategies Table
The following table provides a summary of recommended camera placement strategies for various property types.
| Property Type | Recommended Camera Placement Strategy |
|---|---|
| Large Homes | Multiple cameras strategically positioned at entry points, high-traffic areas, and perimeter to capture complete coverage. |
| Small Apartments | Cameras at entrances, hallways, and common areas to monitor high-traffic zones. |
| Businesses | Cameras covering entrances, exits, parking lots, and high-value areas within the building. |
Field of View and Coverage
Properly positioning outdoor security cameras is crucial for comprehensive coverage, ensuring that no critical areas are overlooked. Understanding field of view (FOV) and how to strategically adjust camera angles is key to maximizing the effectiveness of your security system. This section delves into the significance of FOV, calculation methods, and obstacle mitigation strategies.Optimal camera placement considers not only the area to be monitored but also the specific characteristics of the camera itself, such as its lens type and resolution.
Understanding how to leverage these features can significantly improve the quality and quantity of data captured.
Importance of Field of View (FOV)
Field of view (FOV) directly impacts the area a camera can monitor. A wider FOV captures a larger scene, while a narrower FOV provides greater detail on a smaller area. Choosing the appropriate FOV is essential for a complete security picture. A camera with a narrow FOV might miss critical events in a wide area, while a camera with an extremely wide FOV may produce low-resolution images, making identification difficult.
Calculating Optimal Camera Angle and Distance
Several factors influence the optimal camera angle and distance for comprehensive coverage. The size of the area to be monitored, the camera’s specifications (FOV, resolution), and any obstacles present are critical considerations. Using a camera’s FOV specifications and the distance to the target area, calculations can be performed to determine the necessary camera angle. For example, if a 90-degree FOV camera is positioned 10 meters away, it will capture a wider area compared to a 30-degree FOV camera at the same distance.
Software tools and online calculators can assist in these calculations.
Comparison of Camera Types and FOVs
The table below provides a comparison of different camera types and their typical FOVs. This information helps in selecting the right camera for the specific monitoring needs.
| Camera Type | Typical FOV (horizontal) | Suitable Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Wide-angle | > 60 degrees | Large open areas, parking lots, wide streets |
| Moderate-angle | 40-60 degrees | Medium-sized areas, streets with moderate traffic |
| Narrow-angle | < 40 degrees | Specific areas, high-detail monitoring of individuals or objects |
Minimizing Blind Spots
Strategic camera placement is critical to minimize blind spots. Carefully evaluate the area to identify potential gaps in coverage. Multiple cameras, strategically positioned, can eliminate these gaps. Consider using cameras with varying FOVs to create a comprehensive view of the entire area. A combination of wide-angle and narrow-angle cameras can ensure that no area is overlooked.
Impact of Obstacles on Camera Coverage
Obstacles like trees, buildings, and other structures can significantly affect camera coverage. These obstacles may cause blind spots or obscure parts of the area being monitored. Careful planning and positioning are necessary to overcome these limitations. Consider the height of the obstacle and the camera’s mounting position to ensure clear visibility. Sometimes, repositioning the camera or adding another camera may be necessary to compensate for obstacles.
Adjusting Camera Angles for Maximum Coverage
A well-structured diagram illustrating different camera angles is crucial for optimizing coverage. The diagram should depict how to adjust camera angles to ensure maximum coverage. The diagram below shows a hypothetical example where camera positions are adjusted to ensure complete coverage of a given area, and obstacles are taken into account.[Diagram: Imagine a simple sketch depicting a yard with obstacles (trees, house).
Three cameras are positioned at different angles and heights, with lines indicating the FOV of each camera. The diagram should visually demonstrate how the cameras, strategically placed, eliminate blind spots and cover the entire area.]For example, a camera positioned higher on a building can provide a wider view of a parking lot, while a camera placed lower on a pole can focus on a specific entrance.
This combination of heights and angles helps to maximize coverage.
Lighting Conditions and Visibility

Proper lighting significantly impacts the effectiveness of outdoor security cameras. Adequate illumination allows cameras to capture clear images, crucial for accurate object identification and reliable event recording. Conversely, insufficient or inappropriate lighting can drastically reduce image quality, hindering the camera’s ability to perform its surveillance function. Understanding how light affects camera performance is therefore vital for optimal security system design.Low-light performance is a key factor in selecting cameras for outdoor use.
Cameras with advanced low-light capabilities are essential for capturing clear images in dimly lit areas, contributing to comprehensive coverage and increased safety. The quality of images obtained in low-light conditions directly affects the camera’s ability to detect and identify individuals or objects, and therefore plays a pivotal role in maintaining security.
Impact of Lighting on Camera Performance
Outdoor security cameras are susceptible to variations in light intensity, affecting image quality. Daytime sunlight can cause glare, while nighttime darkness can lead to blurry or indistinct images. These variations impact object recognition and overall camera performance. Camera specifications often include details about their low-light capabilities, enabling informed choices based on specific site conditions.
Optimizing Performance in Low-Light Conditions
Strategic camera placement can significantly enhance performance in low-light conditions. Positioning cameras to maximize the amount of ambient light received is a crucial step. For example, cameras placed near streetlights or buildings with exterior lighting will experience better image quality than those positioned in complete darkness. Furthermore, cameras with built-in infrared (IR) illumination can improve visibility in areas with limited ambient light.
Types of Infrared (IR) Lighting
Different types of IR lighting offer varying levels of effectiveness. Passive IR illumination utilizes ambient light to improve image clarity, while active IR uses dedicated IR LEDs to enhance visibility in complete darkness. Active IR is particularly useful in locations with minimal ambient light, but the range and intensity of the IR illumination must be considered.
Mitigating Shadows and Glare
Shadows and glare can negatively impact camera performance. Positioning cameras to avoid direct sunlight or strategically placing them to minimize shadows is essential. Glare can be mitigated by using anti-glare filters or adjusting camera settings to reduce sensitivity to excessive light. Additionally, strategic placement to minimize reflections from nearby objects can help avoid glare issues.
Examples of Effective Camera Placement in Varied Lighting Conditions
A camera placed on a building’s rooftop, facing a street with streetlights, will have excellent visibility during nighttime hours. Conversely, a camera placed in a densely wooded area with limited ambient light would benefit from an active IR system. In areas with fluctuating lighting conditions, such as near a park or outdoor event space, cameras with advanced low-light capabilities are recommended.
These examples highlight the importance of understanding local lighting conditions when choosing and installing outdoor security cameras.
Table Comparing Camera Models Based on Low-Light Performance
| Camera Model | Low-Light Performance (Rating) | IR Range (meters) | Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Model A | Good | 10 | Active IR, 2MP resolution |
| Model B | Excellent | 20 | Active IR, 4MP resolution, automatic IR adjustment |
| Model C | Fair | 5 | Passive IR, 1MP resolution |
Note: Ratings are subjective and may vary based on specific testing conditions. IR range is an approximation and can be affected by environmental factors.
Network Connectivity and Signal Strength
Robust network connectivity is crucial for outdoor security cameras to reliably transmit video feeds and alerts. A strong signal ensures real-time monitoring, rapid response to events, and uninterrupted data transmission. Poor connectivity can lead to missed alerts, blurry footage, and even camera malfunctions, impacting the effectiveness of the security system. Careful consideration of signal strength and potential interference is vital during the camera placement process.
Importance of Network Connectivity
Reliable network connectivity is essential for the functionality of outdoor security cameras. Continuous data transmission is necessary for live monitoring, recording, and triggering alarms. Interruptions in the signal can result in missed events, hindering the security system’s ability to provide timely alerts and footage. This, in turn, diminishes the camera’s effectiveness in protecting the monitored area.
Optimal Signal Strength Locations
To maximize signal strength, select locations that minimize obstructions and interference from physical structures. Strategically positioning cameras away from large buildings, trees, or metal objects can improve signal quality. Open areas with clear line-of-sight to the wireless router or access point are preferable. This is especially important for cameras with long-range wireless capabilities.
Examples of Optimal Placement for Strong Wireless Signals
For optimal wireless signal strength, consider mounting cameras on elevated structures, such as poles or rooftops. These locations often offer a clearer path to the wireless router. If the camera needs a stronger signal to cover a wider area, positioning it near a router or access point with high-power output is a good option. Similarly, consider using mesh Wi-Fi systems to create a more robust network coverage.
Considering Signal Interference from Nearby Structures
Signal interference can significantly impact camera performance. Large metal structures, thick walls, and dense foliage can obstruct or weaken the wireless signal. Consider the presence of such obstructions when selecting camera locations. A thorough site survey should be conducted to identify potential interference points and to develop strategies to mitigate them.
Testing Signal Strength at Different Locations
To determine the ideal camera placement, test signal strength at various locations. Use a signal strength meter or a dedicated testing application to evaluate the wireless signal. This will help identify areas with optimal coverage and those needing further adjustment. The use of specialized tools is recommended for accurate measurements.
Impact of Factors on Signal Strength
| Factor | Potential Impact on Signal Strength |
|---|---|
| Distance from router/access point | Signal strength decreases with distance. |
| Obstacles (buildings, trees, metal objects) | Obstacles weaken or block the signal. |
| Wireless interference (other devices) | Interference from other wireless devices can reduce signal quality. |
| Signal quality (bandwidth, channel interference) | Lower bandwidth or channel interference may affect signal strength. |
| Weather conditions (rain, snow) | Adverse weather conditions can negatively impact signal strength. |
Security Considerations and Safety

Ensuring the safety and security of your outdoor security cameras is paramount to their effectiveness. Proper installation and consideration of potential risks are crucial for maintaining a robust surveillance system and deterring unwanted activity. This section delves into critical safety aspects, from secure mounting to proactive measures against vandalism.Careful planning and execution during installation minimizes potential hazards and maximizes the cameras’ longevity and effectiveness.
A well-considered security strategy for your outdoor camera system is essential to both deterring and preventing crime.
Important Safety Considerations for Installation
Safe installation procedures are essential for preventing accidents and ensuring the longevity of your outdoor security cameras. Understanding the risks and implementing appropriate safety measures are key to a successful and secure installation. This includes adhering to local building codes and electrical safety regulations.
Secure Mounting and Weatherproofing
Robust mounting is vital for camera stability and longevity. Cameras should be firmly attached to a sturdy structure, resistant to wind and vibration. Weatherproofing is equally crucial. Use weatherproof enclosures and appropriate mounting hardware to protect the camera from rain, snow, and extreme temperatures. Employing high-quality, weather-resistant materials is paramount to ensure camera longevity and functionality in various weather conditions.
Deterrent Positioning Strategies
Strategic placement can act as a powerful deterrent. Position cameras to clearly monitor entrances, exits, and potentially vulnerable areas. Visible cameras in prominent locations send a clear message that the area is under surveillance. Intruders are often deterred by the visual presence of cameras.
Safeguarding Cameras from Vandalism or Theft
Cameras should be installed in a secure location, away from easy access. Consider mounting them high on walls or poles to limit accessibility. Using anti-theft mounting hardware and sturdy enclosures can further protect against vandalism or theft. Employing visible security measures and a sturdy mounting system, and even considering motion-activated lights, can help deter vandalism and theft.
Potential Security Risks Associated with Specific Camera Placements
Carefully assess potential security risks associated with specific camera placements. For instance, placing a camera directly facing a window might allow easy access to the camera. Strategic camera placement in relation to trees or other obstructions is crucial to ensure optimal coverage. Understanding the camera’s field of view and coverage area is critical in avoiding blind spots.
Essential Tools and Materials for Safe Camera Installation
A comprehensive list of tools and materials will ensure a smooth and safe installation process.
- Safety Gear: Eye protection, work gloves, and sturdy footwear are essential for preventing injuries during installation. Safety should always be prioritized when working at heights or with tools.
- Mounting Hardware: Use appropriate screws, anchors, and brackets that are designed for outdoor use and the specific mounting surface. The correct hardware selection is essential for proper installation and ensures the camera remains securely mounted in all weather conditions.
- Weatherproof Enclosures: Protect the camera from the elements with weatherproof enclosures designed for outdoor use. These enclosures ensure the camera functions effectively and lasts for years to come.
- Electrical Components: If the camera requires power, ensure all electrical components meet safety standards and are correctly installed. This includes wiring, outlets, and junction boxes. Correct wiring and electrical connections are vital for safe and effective camera operation.
- Tools: A drill, screwdriver, wire strippers, and a level are necessary for proper installation.
Advanced Camera Features and Configurations
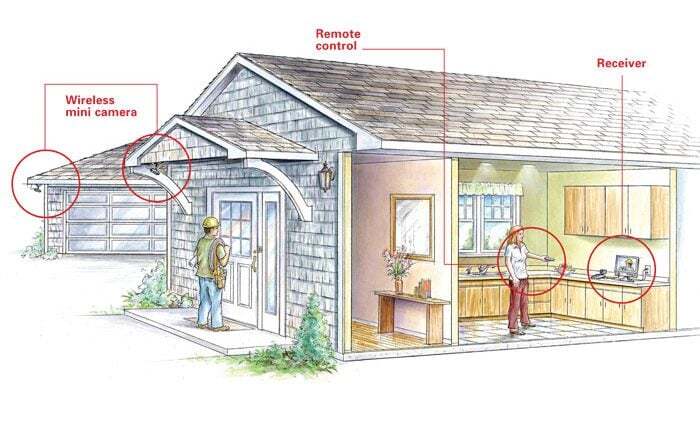
Optimizing outdoor security camera systems often involves leveraging advanced features to enhance coverage, response time, and overall effectiveness. These features, when configured correctly, can significantly improve the system’s ability to detect and respond to potential threats, providing a more robust security solution.Understanding the capabilities of these features, and how to tailor their settings to specific environments, is crucial for achieving maximum security.
This section will delve into motion detection, pan-tilt-zoom, two-way audio, and other advanced functionalities, offering practical guidance on their configuration and application.
Motion Detection
Motion detection is a fundamental feature in modern security cameras. It allows the system to automatically alert users to unusual activity within the monitored area, minimizing false alarms and ensuring prompt response to genuine threats. Proper configuration is essential to avoid excessive alerts, ensuring the system focuses on actual motion, not natural wind or animal movement.Optimizing motion detection settings involves adjusting sensitivity levels, detection zones, and exclusion zones.
Higher sensitivity will trigger alerts for smaller movements but may result in more false alarms. Conversely, lower sensitivity may miss subtle movements. Defining precise detection zones and exclusion zones, such as areas with predictable movement (e.g., a tree swaying in the wind), can further reduce false positives. Careful configuration ensures the system responds only to significant, potentially suspicious activity.
Pan-Tilt-Zoom (PTZ) Cameras
PTZ cameras offer enhanced surveillance capabilities by enabling the camera to adjust its field of view dynamically. This allows for focused observation of specific areas within a larger monitored zone, providing detailed views of suspicious activity.The ability to pan, tilt, and zoom is invaluable in situations where a specific area requires closer inspection. For example, if a motion detection alert occurs in a large parking lot, a PTZ camera can quickly zoom in on the area of interest, facilitating a clearer identification of the event.
Furthermore, this capability provides flexibility in adapting to changing circumstances and maintaining a comprehensive view of the surroundings. Configuration involves defining the camera’s operational range, setting pre-programmed positions, and integrating the PTZ camera into the overall surveillance system.
Two-Way Audio
Two-way audio functionality enables communication between the camera and the user. This feature is particularly valuable for verifying suspicious activity, communicating with individuals within the monitored area, and responding to emergency situations.The camera can be configured to record audio from the monitored area, enabling the user to listen for potential sounds indicative of intrusion or other security breaches. Furthermore, the ability to communicate with individuals present allows for clear instructions or inquiries.
This functionality significantly enhances situational awareness and aids in responding to events in real-time. Configuring two-way audio involves adjusting volume levels, ensuring clear communication, and integrating the audio component into the system’s overall alarm and notification protocols.
Comparative Analysis of Features
| Camera Feature | Potential Benefits | Suitability for Use Cases ||—|—|—|| Motion Detection | Early detection of suspicious activity, reduced false alarms with proper configuration | General surveillance, perimeter monitoring, parking lots, high-traffic areas || Pan-Tilt-Zoom | Enhanced observation of specific areas, detailed views of suspicious activity | High-value assets, areas with large coverage, specific threat analysis || Two-Way Audio | Real-time communication with individuals, verification of events, emergency response | Areas requiring interaction with individuals, businesses with customers, residential security |
Example Configuration: Residential Security
For a residential property, a configuration focusing on motion detection and two-way audio might be appropriate. Three cameras positioned at key entry points, such as the front door and side yard, could be equipped with motion detection sensors. The cameras could be set to moderate sensitivity, with exclusion zones defined for areas with frequent animal activity. Two-way audio would be enabled on all cameras for immediate communication during potential intrusion attempts.
This configuration ensures rapid response to potential threats while minimizing false alarms.
Closure
In conclusion, strategically positioning outdoor security cameras is crucial for comprehensive coverage and optimal security. By carefully considering factors like camera placement strategies, field of view, lighting conditions, network connectivity, and security considerations, you can significantly enhance your property’s protection. This guide has provided a robust framework for implementing a successful security system, enabling you to make informed decisions and maximize the effectiveness of your security investment.