Embark on a journey into the interconnected world of smart home technology. This guide provides a detailed exploration of connecting all your smart devices, from setup to advanced management and troubleshooting. Understanding the benefits, challenges, and various protocols involved is key to harnessing the full potential of your smart home.
This comprehensive guide walks you through the process of identifying, connecting, and managing a diverse range of smart devices. From smart bulbs and thermostats to speakers and hubs, you’ll discover how to create a seamless, centralized system for optimal control and efficiency. Crucially, the guide emphasizes security measures, essential for protecting your connected devices and home network.
Introduction to Smart Home Connectivity

Connecting smart devices in a home creates a network of interconnected appliances, lighting, and other systems. This interconnectedness allows for automation, enhanced convenience, and improved energy efficiency. This system leverages various technologies and protocols to ensure seamless communication between devices.This interconnected system can significantly improve the quality of life in a home by automating tasks, providing real-time insights, and enabling remote control.
However, integrating these devices effectively requires careful planning and consideration of potential vulnerabilities. A well-designed smart home network can offer significant benefits, but it also presents certain challenges that need to be addressed.
Benefits of Connecting Smart Devices
Connecting smart devices in a home offers several advantages. Improved control and automation are key benefits, allowing for the scheduling of tasks, remote operation, and customized responses to environmental changes. Energy efficiency is also a significant benefit. Connected devices can adjust lighting, heating, and cooling based on occupancy and environmental conditions, minimizing energy waste. Enhanced security and safety are further advantages.
Smart devices can monitor the home for intrusions and provide alerts, potentially preventing theft or accidents. Lastly, improved convenience is a key factor, with automation simplifying daily routines and providing greater control over home systems.
Challenges of Smart Home Connectivity
Implementing a smart home network presents several challenges. Security concerns are paramount. Interconnected devices can be vulnerable to hacking, and compromised devices can expose the entire network to risks. Compatibility issues between different manufacturers’ devices can also arise. These issues can lead to communication failures or unexpected behavior.
Complexity in setup and maintenance is another potential challenge. Setting up a complex network of devices can be challenging, and maintaining it may require technical expertise. Privacy concerns are also a factor to consider. Collecting and sharing data from connected devices can raise privacy concerns. These challenges should be carefully evaluated before implementing a smart home network.
Types of Smart Devices and Their Functionalities
Smart devices encompass a wide range of functionalities. Smart lighting systems, such as smart bulbs and LED strips, allow for customizable lighting schemes and energy-efficient operation. Smart thermostats offer precise temperature control and can learn user preferences for optimal comfort and energy savings. Smart security systems include cameras, sensors, and alarms, enabling remote monitoring and alerts for enhanced safety and security.
Smart appliances, like refrigerators and washing machines, provide features such as remote control, scheduling, and status updates. Smart speakers and assistants provide voice control over various home functions, offering hands-free operation and integration with other smart devices. Smart home hubs act as central control points for coordinating different devices.
Common Smart Home Connectivity Protocols
Several protocols are commonly used for smart home connectivity. Z-Wave is a low-power, wireless protocol ideal for home automation. Zigbee is another popular wireless protocol known for its reliability and energy efficiency. Wi-Fi is a widely used protocol for connecting smart devices to the internet, allowing for remote control and access. Thread is a low-power, mesh-based protocol specifically designed for smart home networks, offering robust communication and security.
These protocols are crucial for ensuring seamless communication and reliable operation within a smart home network.
Identifying and Connecting Devices

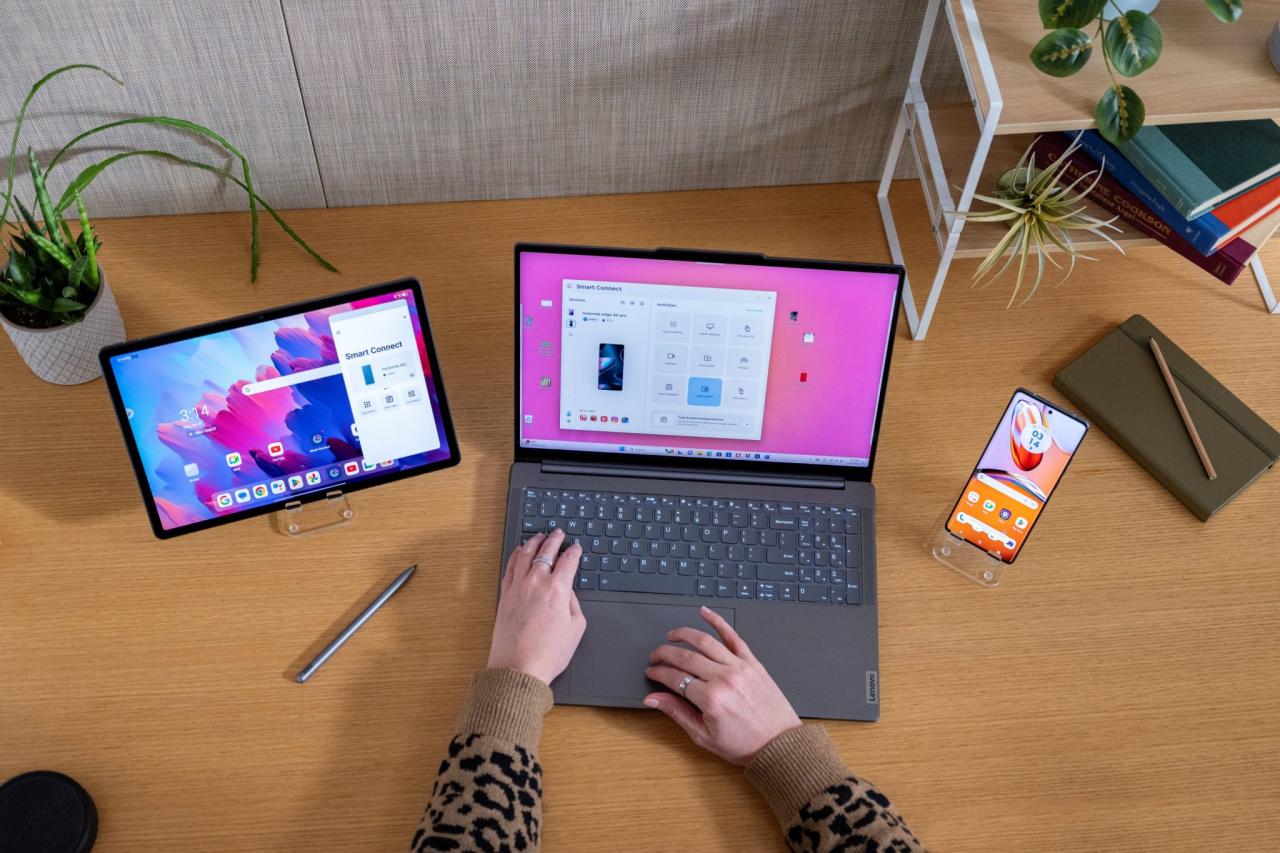
Connecting smart devices effectively is crucial for a seamless smart home experience. This process involves several key steps, from identifying available devices to establishing reliable communication channels. Understanding the various methods and protocols used will allow you to build a well-integrated and functional smart home.Device discovery and pairing are often facilitated by readily available tools and technologies, offering convenient and efficient methods for setting up smart home components.
This ensures that all your devices are effectively connected and interacting seamlessly with each other and your network.
Methods for Device Discovery and Location
Several methods facilitate locating and identifying devices on a network. These methods range from simple network scans to more sophisticated techniques involving dedicated discovery protocols. The choice of method depends on the specific device and the network environment. For example, some devices utilize Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) for local discovery, while others rely on Wi-Fi for broader network visibility.
This diversity ensures flexibility and adaptability to various situations.
Protocols for Device Communication and Interoperability
Various communication protocols underpin the interaction between smart devices. These protocols enable interoperability, allowing different devices from various manufacturers to communicate and work together. Common protocols include Wi-Fi, Z-Wave, Zigbee, and Bluetooth. Understanding these protocols helps in selecting devices that can integrate seamlessly with existing systems and avoid compatibility issues. For instance, Z-Wave is often preferred for its robustness and reliability in transmitting data over longer distances.
Approaches to Device Pairing and Setup
Different approaches to device pairing and setup exist. Some devices utilize a simple QR code scan, while others require entering specific configuration parameters into a mobile application or the device itself. The chosen method depends on the device’s complexity and the desired level of user interaction. Many smart devices leverage user-friendly interfaces, making the pairing process intuitive and straightforward.
This ensures ease of use for users of varying technical backgrounds.
Connecting a Smart Bulb
Connecting a smart bulb involves a few simple steps. First, ensure the bulb is compatible with your chosen smart home system. Then, install the relevant mobile application or use a web-based interface to set up the device. Next, connect the bulb to your Wi-Fi network by providing the network credentials. Once the connection is established, the bulb will appear in your smart home app, ready for use.
Connecting a Smart Thermostat
Connecting a smart thermostat often involves similar steps as connecting a smart bulb. First, download the appropriate app and ensure compatibility with your thermostat model. Then, follow the on-screen prompts to set up the thermostat, including configuring the network connection. This may involve connecting to your home Wi-Fi network. Finally, calibrate the thermostat settings according to your preferences.
Connecting a Smart Speaker
Connecting a smart speaker typically involves a straightforward process. First, ensure the speaker is compatible with your smart home system. Next, download the appropriate app and follow the on-screen prompts to set up the device. Finally, connect the speaker to your Wi-Fi network, and it will be ready to use.
Common Device Connection Issues and Solutions
| Device Type | Connection Issue | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Smart Bulb | Incorrect Wi-Fi credentials | Verify Wi-Fi password |
| Smart Thermostat | No internet connection | Check network connectivity |
| Smart Speaker | Can’t find network | Restart router/modem |
Establishing a Centralized System
Centralized systems offer a streamlined approach to managing your smart devices, providing a single point of control and simplifying interactions. This approach enhances the overall user experience by unifying device management and automating tasks. This section will detail the various options for creating a central hub or platform, explore cloud-based platforms, and demonstrate configuration methods.A well-established centralized system can significantly improve the efficiency and effectiveness of your smart home.
It allows for seamless integration and automation of tasks, such as scheduling lights to turn on at sunset or adjusting the thermostat based on your location. A unified platform provides a comprehensive overview of all connected devices, enabling you to monitor and control them remotely.
Different Options for Central Hubs
A central hub acts as the command center for your smart devices, allowing you to control and monitor them from a single interface. Several options are available, ranging from dedicated smart home hubs to cloud-based platforms.
- Dedicated Smart Home Hubs: These hubs, such as Amazon Echo, Google Home, or SmartThings Hub, provide a physical device that connects to your network and acts as a central control point for compatible smart devices. These hubs often offer a user-friendly interface for device management and integration.
- Cloud-Based Platforms: Many cloud-based services offer comprehensive platforms for managing smart devices. These platforms provide a centralized system for controlling various devices and automating tasks, often with greater scalability and flexibility compared to dedicated hubs. They typically integrate with various smart home devices through their APIs.
Cloud-Based Platforms for Device Management
Cloud-based platforms offer a convenient way to manage smart devices remotely. They provide a comprehensive dashboard for controlling and monitoring connected devices, often with advanced features such as automation rules and remote access.
- Pros of Cloud-Based Platforms: Cloud platforms offer scalability and flexibility, supporting a wide range of devices. They typically offer extensive automation capabilities and remote access, allowing you to control your home from anywhere. Cloud platforms often provide security features, such as data encryption and user authentication.
- Cons of Cloud-Based Platforms: Cloud-based platforms can sometimes have limited support for certain devices, requiring a specific interface. Security is paramount, and you need to ensure your chosen platform adheres to industry security standards and you carefully review its privacy policy. Connectivity issues may occur if your internet connection is unreliable. Depending on the platform, subscription fees may be involved.
Configuring a Central System for Device Control
Configuring a central system for device control typically involves connecting your devices to the chosen hub or platform, then setting up the desired configurations. Instructions often vary based on the platform, but common steps include:
- Device Pairing: This typically involves downloading the platform’s app, creating an account, and connecting your devices to the system. The specific steps will vary depending on the device and platform. Follow the platform’s instructions carefully to avoid any issues.
- Automation Rules: Once your devices are connected, you can create automation rules to automate tasks based on schedules, sensors, or other triggers. This is a crucial aspect of a centralized system as it enhances convenience and efficiency.
- Remote Access: Most platforms provide remote access, enabling you to control your home devices from anywhere with an internet connection. This is beneficial for managing your smart home when you are away from home.
Comparison of Smart Home Hubs
The following table compares some popular smart home hubs based on ease of use, security, and cost.
| Hub | Ease of Use | Security | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amazon Echo | Generally user-friendly, intuitive interface | Strong security features, regular updates | Primarily through device purchases and subscriptions |
| Google Home | Straightforward setup, simple control | Robust security measures, regularly updated | Primarily through device purchases and subscriptions |
| SmartThings Hub | Requires more technical understanding, potentially more advanced features | Strong security measures, regular updates | Typically a one-time purchase, with potential subscriptions for advanced features |
Implementing Security Measures

Securing your smart home network is paramount to protecting your personal information and ensuring the smooth operation of your connected devices. A compromised system can lead to unauthorized access, data breaches, and even financial loss. Robust security measures are crucial for maintaining a safe and reliable smart home environment.Implementing comprehensive security protocols is not merely a technical necessity; it’s a proactive measure to safeguard your privacy and well-being.
A well-fortified smart home network reduces the risk of various security threats, ensuring a seamless and secure experience for all users.
Importance of Security in a Connected Smart Home
A secure smart home network is essential for protecting sensitive data and preventing unauthorized access to your devices and network. Compromised smart home systems can expose personal information, including financial details, health records, and communication logs. This sensitive information is vulnerable to various cyber threats, including hacking, malware, and data breaches.
Different Security Measures for Protecting Connected Devices
Implementing various security measures is crucial to mitigate potential risks. These include strong passwords, multi-factor authentication, regular software updates, and robust network configurations. Furthermore, using trusted applications and services is critical to maintaining a secure environment.
- Strong Passwords: Employing complex and unique passwords for each device and account is a fundamental security practice. Avoid easily guessable passwords like “password123” or your birthdate. A strong password includes a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols. The length of the password should also be considered. Using a password manager can aid in generating and managing strong, unique passwords.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Enabling MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring more than one form of verification to access your accounts. This could include a code sent to your phone or an authentication app. By requiring both a password and a second verification step, MFA significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access.
- Regular Software Updates: Keeping the software of your smart devices and the network router up-to-date is essential. Software updates often include security patches that address vulnerabilities and prevent malicious attacks. Failure to update can leave your devices susceptible to exploits.
- Robust Network Configurations: Configuring a strong Wi-Fi network with a strong password, disabling unnecessary network features, and using a Virtual Private Network (VPN) can bolster security. Using a VPN encrypts your internet traffic, adding an extra layer of security.
Step-by-Step Procedure for Securing a Smart Home Network
A methodical approach to securing your smart home network is essential. This involves several steps:
- Assess Your Existing Network: Evaluate your current network configuration, including the types of devices connected and their security settings.
- Update Software: Ensure that all connected devices and your router’s firmware are updated to the latest versions.
- Strong Passwords: Create strong and unique passwords for each device and account, employing a password manager if necessary.
- Enable MFA: Wherever possible, activate multi-factor authentication to add an extra layer of security.
- Network Segmentation: Consider segmenting your network to isolate sensitive devices and create separate networks for different purposes.
- Regular Monitoring: Regularly monitor your network for any unusual activity.
Common Security Vulnerabilities and Risks
Several vulnerabilities exist in smart home systems. These include weak passwords, outdated software, and inadequate network configurations. Lack of multi-factor authentication and poor device security practices increase the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches. In a connected smart home, the interconnection of devices creates a potential attack surface, requiring vigilance to mitigate these risks.
Checklist for Securing Devices Before Connecting
A checklist helps ensure comprehensive security measures are implemented before connecting any device to the network.
- Verify the device’s security settings, such as password complexity and multi-factor authentication options.
- Confirm the device’s software is up-to-date with the latest security patches.
- Assess the device’s data storage and transmission protocols for potential vulnerabilities.
- Review the device’s privacy policy and terms of service to understand data handling practices.
- Consider using a VPN to encrypt data transmitted over the network.
Controlling and Managing Connected Devices
Effective management of smart home devices hinges on centralized control and insightful monitoring. This allows users to seamlessly operate their ecosystem, optimize energy consumption, and automate tasks, enhancing convenience and efficiency. Centralized control, combined with sophisticated monitoring, empowers homeowners to take full advantage of their smart home’s capabilities.Centralized control provides a unified interface for managing various smart devices, allowing users to interact with their home ecosystem effortlessly.
Monitoring functionalities empower users to track device usage patterns and energy consumption, leading to informed decisions and potential cost savings. Automation further enhances user experience, enabling predefined actions based on various triggers and conditions.
Centralized Control Methods
A wide array of methods facilitates control from a central point. These range from dedicated mobile applications to voice assistants, offering diverse approaches tailored to individual preferences. This flexibility ensures users can choose the control method that best suits their needs and lifestyle. For example, a mobile app can provide a comprehensive overview of all connected devices, allowing users to adjust settings, control individual appliances, and monitor energy consumption in real-time.
Monitoring Device Usage and Energy Consumption
Comprehensive monitoring tools provide valuable insights into device usage patterns and energy consumption. Detailed reports allow users to identify areas for optimization and potential cost savings. Real-time data dashboards offer an immediate overview of device activity, facilitating proactive management. Smart thermostats, for instance, can track temperature adjustments and energy usage, enabling users to fine-tune settings for optimal comfort and efficiency.
Energy consumption data can be presented visually through graphs and charts for better understanding.
Automated Task Execution
Automation empowers users to streamline their daily routines by defining pre-programmed actions based on specific conditions. This feature simplifies tasks and optimizes energy consumption. For example, turning on the lights automatically when the user enters a room or adjusting the thermostat based on the time of day are common applications of automation. These automated responses can significantly enhance comfort and convenience.
Complex Automation Scenarios
Advanced automation scenarios can orchestrate multiple devices to achieve more complex objectives. Imagine a system that automatically adjusts the lighting, temperature, and music based on the time of day and the user’s schedule. Integration with smart calendars allows for seamless scheduling and proactive responses. A more complex example could involve a system that triggers the coffee maker to start brewing, adjusts the lighting to a brighter setting, and plays a specific playlist upon waking.
Controlling Specific Device Types
Specific control methods cater to different device types. For instance, smart lighting systems typically offer control through mobile applications, voice commands, or pre-programmed schedules. Smart thermostats often feature intuitive interfaces for adjusting temperature settings and scheduling heating and cooling cycles. Smart security systems often offer remote monitoring and control via dedicated applications or voice commands. This tailored approach ensures optimal control and management for each device category.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Maintaining a seamless smart home experience requires proactive troubleshooting. Addressing connectivity problems and device malfunctions promptly can prevent frustration and ensure all your smart devices operate as intended. This section Artikels common issues and provides practical solutions to help you resolve them effectively.
Common Connection Problems and Solutions
Troubleshooting connection problems is crucial for a smooth smart home experience. Understanding the common causes and corresponding solutions can save time and effort.
- Interference from other devices: Wi-Fi signals can be affected by other electronic devices operating in the same frequency range. Using a different frequency band (if available) or repositioning the router can often resolve the issue.
- Weak or unstable Wi-Fi signal: Devices may struggle to connect or maintain a connection if the Wi-Fi signal is weak or unreliable. Moving the device closer to the router or using a Wi-Fi extender can improve signal strength.
- Incorrect network settings: Misconfigured network settings, such as incorrect passwords or SSIDs, can prevent devices from connecting to the network. Double-checking the network settings on both the router and the device is essential.
- Outdated firmware: Outdated firmware can cause compatibility issues and connectivity problems. Ensuring all devices have the latest firmware updates can significantly improve performance and stability.
- Power fluctuations: Brief power outages or inconsistent power supply can disrupt connections and cause devices to malfunction. Using surge protectors or ensuring a stable power supply can help mitigate this issue.
Troubleshooting Connectivity Problems Between Devices
Identifying the root cause of connectivity problems between devices requires a systematic approach. By isolating the potential problems, one can effectively diagnose and rectify the issues.
- Check device logs: Many smart devices provide detailed logs that can help identify the source of connectivity problems. Reviewing these logs can provide insights into specific errors or issues.
- Verify network connectivity: Ensure that all devices are properly connected to the network and have the necessary permissions to communicate with each other. Verify that all devices are on the same network.
- Test individual connections: Test the connection between each device and the network individually. This helps isolate if a particular device is the source of the issue.
- Restart devices and router: A simple restart of devices and the router can resolve temporary connectivity issues. This action often clears cached data and re-establishes connections.
Typical Device Malfunctions and Their Causes
Understanding the potential causes of device malfunctions can help in identifying and resolving them efficiently. Recognizing the signs and understanding the root causes are crucial steps in troubleshooting.
- Device not responding: A device not responding can be due to various factors, such as insufficient power, software glitches, or connectivity issues. Restarting the device or checking for updates is often a good first step.
- Slow response times: Slow response times can be caused by high network traffic, device overload, or insufficient processing power. Monitoring network traffic and optimizing device usage can help improve response times.
- Unexpected disconnections: Unexpected disconnections can result from unstable Wi-Fi signals, interference, or issues with the network itself. Using a stronger Wi-Fi signal, checking for interference, or restarting the router can resolve the issue.
Steps to Resolve Issues with Individual Devices
Troubleshooting individual device problems involves a step-by-step approach to identify and resolve the issue. Each device may require specific steps for resolution.
- Check device manuals: Refer to the device’s manual for troubleshooting steps specific to the device model. Manuals often contain valuable information on resolving common issues.
- Contact manufacturer support: If the problem persists, contacting the manufacturer’s support team can provide specialized assistance tailored to the specific device.
- Update device software: Updating the device software can often resolve compatibility issues and improve performance. Checking for software updates is a crucial troubleshooting step.
Error Codes and Explanations
A table of common error codes and their corresponding explanations can be a valuable resource in troubleshooting. This can help quickly identify and resolve the problem.
| Error Code | Explanation |
|---|---|
| 101 | Incorrect network password |
| 202 | Device not connected to the network |
| 303 | Insufficient power supply |
| 404 | Communication failure |
| 505 | Firmware update required |
Future Trends in Smart Home Connectivity
The smart home is rapidly evolving, driven by advancements in technology and a growing demand for integrated and intuitive living experiences. Future trends are focused on enhancing the seamlessness and intelligence of connected devices, creating more personalized and responsive environments. This evolution will encompass not only the physical connectivity but also the data processing and application of that connectivity.The future of smart home connectivity will be characterized by a convergence of technologies, resulting in a more sophisticated and interconnected ecosystem.
This interconnectedness will be pivotal in creating environments that anticipate and respond to user needs, improving overall efficiency and comfort.
Emerging Technologies and Their Impact
Emerging technologies, such as the Internet of Things (IoT) and Artificial Intelligence (AI), are significantly impacting smart home connectivity. IoT facilitates the communication between various devices, while AI enables advanced automation and personalized control. The integration of these technologies leads to a more sophisticated and intuitive user experience. Examples include AI-powered voice assistants that learn user preferences and adjust settings automatically, and IoT-enabled appliances that communicate with each other to optimize energy consumption.
Potential Future of Connecting Devices and Systems
The future of connecting devices and systems in smart homes will see an increase in interoperability and seamless integration. Standards for communication between different brands and types of devices will become more standardized and widespread, allowing for a greater degree of flexibility and customization. Furthermore, the development of cloud-based platforms will allow for centralized management and control of connected devices, irrespective of their brand or manufacturer.
This centralized control will further enhance the ease of use and management of the smart home ecosystem.
Future Developments in Smart Home Technology
Future developments in smart home technology will emphasize personalized experiences and proactive responses to user needs. This will involve the development of predictive maintenance, where devices anticipate potential issues and proactively schedule repairs or maintenance. Moreover, the evolution of energy management systems will optimize energy consumption and cost savings based on real-time data and user preferences. Further development of home security systems that integrate with other smart devices to provide comprehensive monitoring and protection is another example.
Innovative Approaches to Smart Home Connectivity
Innovative approaches to smart home connectivity will include the development of more secure and robust communication protocols. These protocols will address the vulnerabilities of existing systems, improving overall security and reliability. For instance, technologies like blockchain and encryption will play a crucial role in ensuring the confidentiality and integrity of data exchanged between devices. This will foster greater user trust in the security of their smart home environment.
Another approach is to create more intuitive and user-friendly interfaces for managing connected devices. This will make the smart home more accessible to a wider range of users.
Summary of Current and Future Standards for Interoperability
Current standards for smart home interoperability, such as Z-Wave, Zigbee, and Wi-Fi, are being expanded and improved. Future standards will likely focus on a more unified and streamlined approach to device communication. This unified approach will allow for greater flexibility and integration of devices from different manufacturers. For example, the development of a universal communication protocol that is supported by a wide range of devices could enable a more seamless and standardized experience.
In summary, future standards will prioritize interoperability, security, and ease of use.
Final Conclusion
In conclusion, connecting all your smart devices together can transform your home into a sophisticated, automated space. This guide has provided a detailed roadmap for navigating the process, from initial setup to ongoing maintenance and troubleshooting. By understanding the various protocols, security considerations, and management strategies, you can confidently leverage the power of a truly connected smart home.
The future of smart home technology is promising, and this guide equips you with the knowledge to embrace its possibilities.